You are here
Content
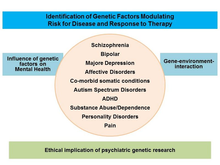
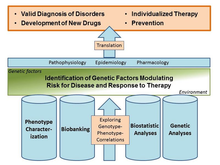
Genetic Epidemiology in Psychiatry
The Department of Genetic Epidemiology in Psychiatry investigates the biological and environmental basis of psychiatric disorders as well as the interaction of these two factors. Since psychiatric genetic research touches on a number of ethically sensitive issues, the department also intensively investigates the ethical questions surrounding this type of research with a science-based approach.
Subject areas and research focus of the department
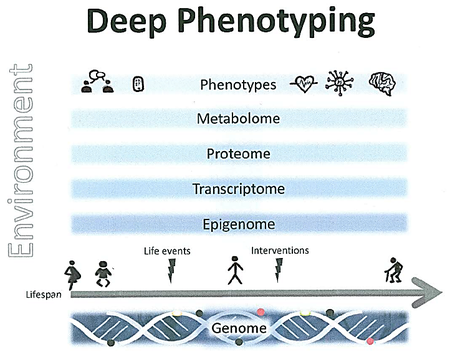
- intense, longitudinal phenotyping with the simultaneous assessment of environmental factors („deep phenotyping“)
- biobanking with various biomaterials
- biostatistical analysis of genetic und phenotype data
- ethical aspects of psychiatric genetic research
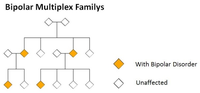
Example 1: Families with a high genetic burden
Studies in families with a high prevalence of Bipolar Affective Disorder, where the hereditary pattern suggests the presence of a few rare disease mutations with a strong causal effect, show that, in fact, many variants with small effects and which are also found in healthy people also play a role in the disease etiology.
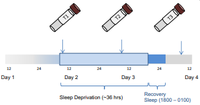
Example 2: Intervention study of depressed patients undergoing therapeutic sleep deprivation
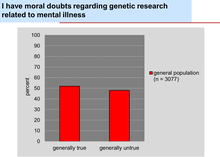
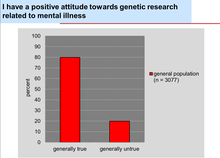
Example 3: Controversial opinions and ambivalence with regard to psychiatric genetic research
A fundamental ethical principle in the context of psychiatric genetic research as well as future clinical applications is the respect for the autonomy of a person to decide if and which genetic analyses will be carried out and to whom access to their genetic data is granted. However, experience has shown that the implementation of this principle in real-life situations in the field of psychiatric genetic research is complex, as people’s opinions are often characterized by ambivalence.
While 75% of all respondents said, for example, that they always wanted to be informed about their test results, only 40% responded in a further question that they only wanted to be informed if it involved a treatable, preventable, or serious illness.
Even with regard to the duty and liberty of the attending physician to share results of genetic examinations against the will of the subject, ambivalent attitudes prevailed conditional upon the available options for treatment and preventability of the illness.
National and International Joint Research Projects
Heidelberg University GRK 2350/1: Graduiertenkolleg - Impact of Adverse Childhood Experiences on Psychosocial and Somatic Conditions Across the Lifespan. Schmahl C. 04/2018-09/2022.
German Research Foundation TRR 265/1: ReCoDe - Losing and Regaining Control over Drug Intake: from trajectories to mechanisms to interventions. TP S01 06/2019-05/2022.
German Research Foundation WI 3439/3-2: FOR2107 - Neurobiology of affective disorders: A translational perspective on brain structure and function, WP5: (Epi-)Genetics/ gene expression. 12/2018-11/2021.
Federal Ministry of Education and Research 01EE1406C: AERIAL - Addiction: Early Recognition and Intervention Across the Lifespan, TP7: Epigenetics and alcohol use disorders. 02/2015-02/2020.
Federal Ministry of Education and Research 01EE1409C: ASD-Net - Autism Spectrum Disorder across the lifespan: From a better etiological understanding, through valid diagnosis, to more effective health care, Service module: (Epi)Genetics and imaging genetics in ASD. 02/2015-12/2020.
Federal Ministry of Education and Research 031L0190A: Target-OXY - Towards Targeted Oxytocin Treatment in Alcohol Addiction, WP5: In silico approaches for ILD and app-based EMA data preclinical phase II testing. 06/2019-05/2022
Federal Ministry of Education and Research 01ZX1909A: SysMedSUDs - A systems-medicine approach towards distinct and shared resilience and pathological mechanisms of substance use disorders. 11/2019-10/2022
Federal Ministry of Education and Research 01EW1904: EMBED - Impact of Early life MetaBolic and psychosocial strEss on susceptibility to mental Disorders; from converging epigenetic signatures to novel targets for therapeutic intervention. 06/2019-05/2022.
Federal Ministry of Education and Research 01EW1810: SYNSCHIZ - Linking synaptic dysfunction to disease mechanisms in schizophrenia - a multilevel investigation, WP1: Gene discovery, WP5: Innovation, IPR protection and commercial exploitation. 08/2018-07/2021.
Selected Publications
- Witt SH, Streit F, Jungkunz M, Frank J, Awasthi S, (…) Rujescu D, Lieb K, Roepke S, Schmahl C, Bohus M, Rietschel M.. (2017) Genome-wide association study of borderline personality disorder reveals genetic overlap with bipolar disorder, major depression and schizophrenia. Transl Psychiatry. 7(6):e1155. doi: 10.1038/tp.2017.115.
- Witt, SH; Frank, J; Frischknecht, U; Treutlein, J; Streit, F; Foo, JC; Sirignano, L; Dukal, H; Degenhardt, F; Koopmann, A; Hoffmann, S; Koller, G; Pogarell, O; Preuss, U; Zill, P; Adorjan, K; Nöthen, M; Spanagel, R; Kiefer, F; Rietschel, M. (2020) Acute alcohol withdrawal and recovery lead to profound changes in DNA methylation profiles – a longitudinal clinical study. Addiction. In publication.
- Stahl EA, Breen G, Forstner AJ, McQuillin A, (…)Sklar P; Bipolar Disorder Working Group of the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium. (2019) Genome-wide association study identifies 30 loci associated with bipolar disorder. Nat Genet. 51(5):793-803. doi: 10.1038/s41588-019-0397-8.
- Strohmaier J, Witt SH, Frank J, Lemme N, Flatau L, Streit F, Foo JC, Reitt M, Rujescu D, Schulze TG, Lanzerath D, Illes F, Degenhardt F, Rietschel M. (2019) Attitudes toward the right to autonomous decision-making in psychiatric genetic testing: Controversial and context-dependent. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 180(8):555-565. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.b.32724.
- Send TS, Bardtke S, Gilles M, Wolf IAC, Sütterlin MW, Wudy SA, Wang R, Laucht M, Witt SH, Rietschel M, Streit F, Deuschle M. (2019) Prenatal maternal stress is associated with lower cortisol and cortisone levels in the first morning urine of 45-month-old children. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 103:219-224. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2019.01.017.
- Foo JC, Streit F, Frank J, Witt SH, Treutlein J; Major Depressive Disorder Working Group of the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium, Baune BT, Moebus S, Jöckel KH, Forstner AJ, Nöthen MM, Rietschel M, Sartorius A, Kranaster L. (2019) Evidence for increased genetic risk load for major depression in patients assigned to electroconvulsive therapy. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 180(1):35-45. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.b.32700.
- Walters RK, Polimanti R, Johnson EC, McClintick JN, (…),Gelernter J, Edenberg HJ, Agrawal A. (2018) Transancestral GWAS of alcohol dependence reveals common genetic underpinnings with psychiatric disorders. Nat Neurosci. 21(12):1656-1669. doi: 10.1038/s41593-018-0275-1.
- Brainstorm Consortium, Anttila V, Bulik-Sullivan B, Finucane HK, Walters RK, (…), Edenberg HJ, Murray R. (2018) Analysis of shared heritability in common disorders of the brain. Science. 360(6395). pii: eaap8757. doi: 10.1126/science.aap8757.
- Bipolar Disorder and Schizophrenia Working Group of the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium. Electronic address: douglas.ruderfer@vanderbilt.edu; Bipolar Disorder and Schizophrenia Working Group of the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium. (2018) Genomic Dissection of Bipolar Disorder and Schizophrenia, Including 28 Subphenotypes. Cell. 173(7):1705-1715.e16. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.05.046.
- Witt SH, Frank J, Gilles M, Lang M, Treutlein J, Streit F, Wolf IAC, Peus V, Scharnholz B, Send TS, Heilmann-Heimbach S, Sivalingam S, Dukal H, Strohmaier J, Sütterlin M, Arloth J, Laucht M, Nöthen MM, Deuschle M, Rietschel M. (2018) Impact on birth weight of maternal smoking throughout pregnancy mediated by DNA methylation. BMC Genomics. 19(1):290. doi: 10.1186/s12864-018-4652-7.
Context Column
Contact
PD Dr. Stephanie Witt
Genetic Epidemiology in Psychiatry
Central Institute of Mental Health
J5
68159 Mannheim
Phone +49 621 1703-6056
stephanie.witt@zi-mannheim.de