You are here
Content
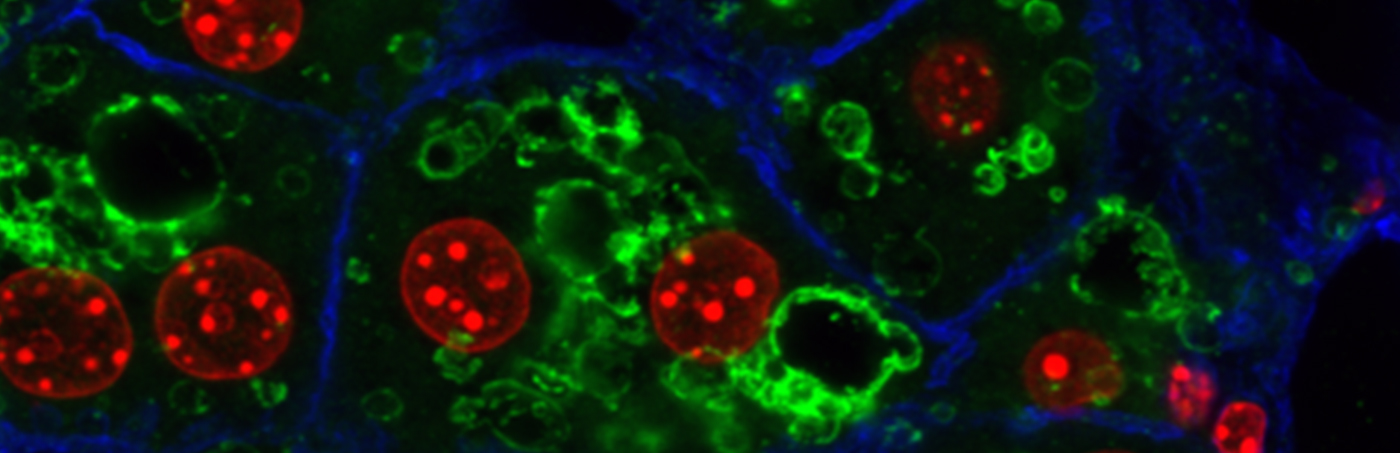
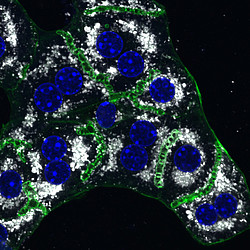
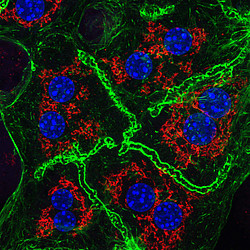
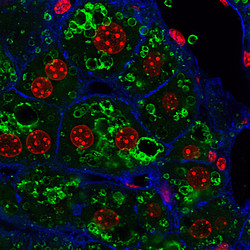
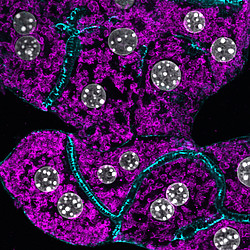
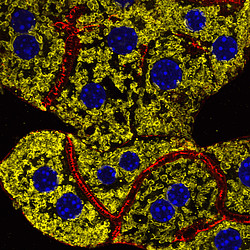
The global prevalence of obesity and type-2 diabetes (T2D) has reached a qualified epidemic stage. This presents a heavy burden on the society and thus it is essential to find novel mechanisms and targets that could be utilized for potential treatment strategies. In light of this demand, recent evidence has begun to support a role for intracellular membrane trafficking in metabolic homeostasis. Membrane transport is an essential physiological process responsible for the sorting and distribution of signaling receptors, membrane transporters and hormones or other ligands between different intracellular compartments and the plasma membrane. Dysregulation of intracellular transport is connected with many human diseases, including cancer, neurodegeneration, immune deficiencies, and recently metabolic diseases, such as type-2 diabetes and its associated complications. Thus, we want to understand how intracellular membrane trafficking and metabolism influence and regulate each other and study the function of the endo-lysosomal system in liver physiology and pathophysiology of diabetes and obesity.
Context Column
Basic Principles of Metabolic
Diseases
European Center for Angioscience (ECAS)
Medical Faculty Mannheim
Heidelberg University
Tridomus C (Level 5)
Ludolf-Krehl-Str. 13-17
68167 Mannheim
Head