Research
Deciphering immune-regulatory functions of lymphatic endothelial cells in lymph nodes
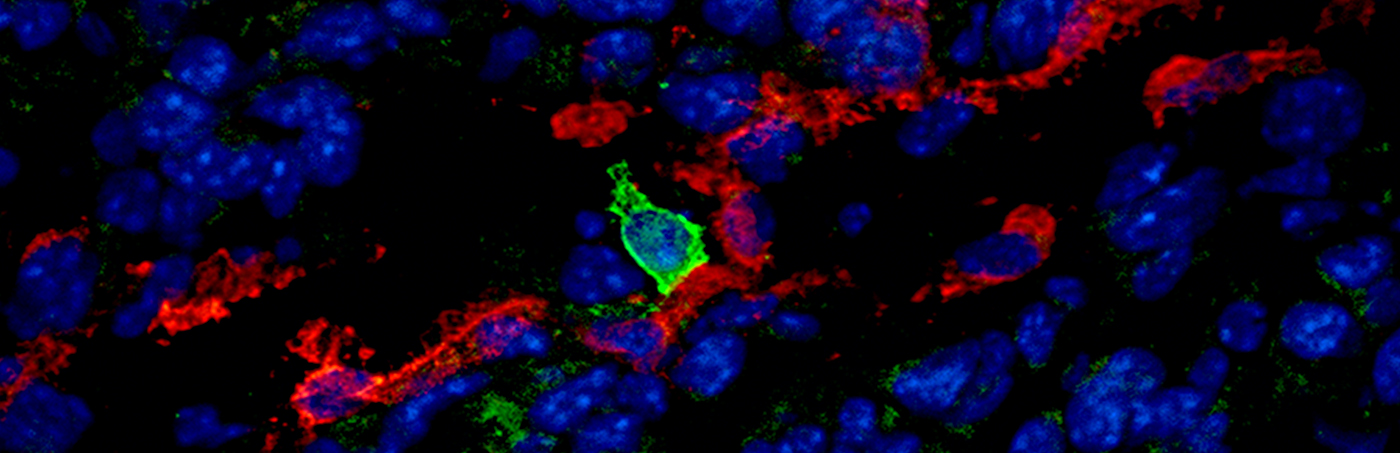
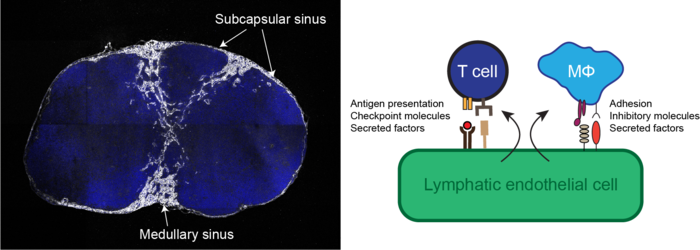
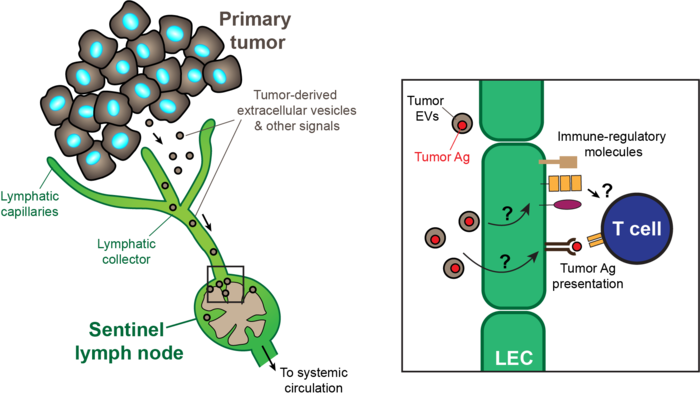
Single-cell transcriptional analysis has demonstrated that lymph node-resident lymphatic endothelial cells are heterogenous, comprising at least three subsets conserved in mice and human that populate the floor and ceiling of the subcapsular sinus as well as medullary sinuses. Recently, we found that these subsets dynamically and differentially respond to pathological conditions, for instance in conditions of chronic dermatitis and tumor growth. Using clinically relevant animal disease models we aim to comprehensively map the heterogeneity and phenotypic responses of lymph node-resident lymphatic endothelial cells in cancer, autoimmunity, and chronic inflammatory diseases, in order to identify immune-regulatory pathways that can be exploited therapeutically.