Sie befinden sich hier
Inhalt
We focus on Natural Killer (NK) cells and monocytes/macrophages that function at the forefront of immune responses. We expect that the obtained mechanistic knowledge will be instrumental for the design of innovative therapies of cancer and in conditions of tissue damage, where these checkpoints could be therapeutically blocked or fostered, respectively. Consortium members benefit from complementary expertise in innate immunity, a common focus on complex immune processes, and from sharing cutting-edge experimental methods including sophisticated single-cell RNAseq analyses, proteomics, metabolomics and multiparameter flow cytometry. Our goals are tackled by interdisciplinary collaborations of experts in different fields of innate immunity and with structured cooperations between basic and clinical researchers. To benefit from complementary expertise in innate immunity, GRK 2727 collaborates with pioneers in the field of innate immunity from the Karolinska Institute (KI) in Stockholm and Vienna University.
A: Cell intrinsic mechanisms of innate immune checkpoints
A.1: Gene expression checkpoints
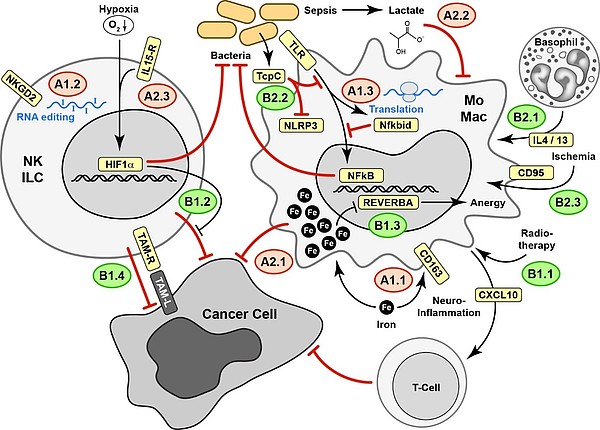
- A.1.1: Decoding and regulating iron homeostasis in myeloid cells in neuroinflammation
- A.1.2: Epitranscriptomic control of NK cell function
- A.1.3: Translation control of checkpoint gene expression
A.2: Metabolic checkpoints
- A.2.1: Red blood cells and iron as checkpoints of macrophage polarization and NK cell reactivity
- A.2.2: Extracellular lactate as an inhibitory checkpoint of monocyte activation
- A.2.3: Understanding hypoxia-immune signaling interactions in human NK cells
B: Modulation of innate immune reactivity in disease
B.1: Cancer
- B.1.1: Modulating innate checkpoints for brain tumor immunotherapy
- B.1.2: HIF-1α-mediated regulation of liver Innate Lymphoid Cell (ILC) responses
- B.1.3: Targeting nuclear receptor checkpoints in tumor-associated macrophages from colorectal cancer
- B.1.4: Analysis of the immune checkpoint function of TAM receptors in anti-tumor NK cell response
B.2: Damage
- B.2.1: Governors of innate immunity responses after myocardial infarction: Identifying crucial healing mechanisms
- B.2.2: TIR-containing protein C of uropathogenic Escherichia coli as regulator of innate immune checkpoints
- B.2.3: CD95-Checkpoint to fine-tune innate immunity for direct efficient repair of the diseased CNS
Kontextspalte
GRK 2727/1 – InCheck
„Innate Immune Checkpoints in Cancer and Tissue Damage"
TPMA2, 2. OG
Franz-Volhard-Str. 6
68167 Mannheim
Phone +49 621 383-71509
Fax +49 621 383-71506
grk2727@medma.uni-heidelberg.de
Twitter GRK 2727: @grk2727