Sie befinden sich hier
Inhalt
We are interested in altered signal transduction in cardiovascular diseases to identify and characterize novel therapeutic targets. Currently there are three major research topics.
Nucleoside diphosphate kinase and its role cardiovascular diseases
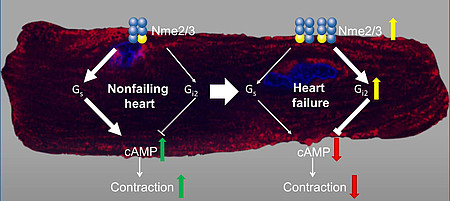
NDPK contributes to the activation of G proteins by providing the required GTP. Especially, the isoform NDPK B is additionally required for the formation of caveolae and can further regulate the function of other proteins, e. g. the potassium channel KCa3.1, by phosphorylation on histidine residues. The hetero-oligomerization with NDPK C governs the GPCR-independent activation of G proteins in the non-failing and failing myocardium.
By the use of NDPK B deficient mice as well as NDPK B depletion in zebrafish embryos as well as cultured endothelial and vascular smooth muscle cells, we characterize the role of this enzyme in vascular biology. As we obtained results indicating its contribution to the development of diabetic retinopathy, alterations in angiogenesis and the formation of a neointima after vessel injury, we intend to establish NDPK Band NDPK C as novel molecular targets for small molecule inhibitors.
Guanine nucleotide exchange factors in vascular function
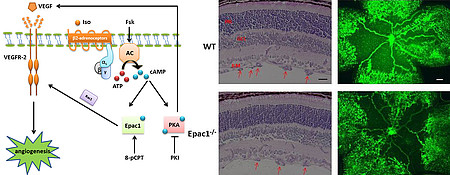
Guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) are proteins catalyzing the activation of monomeric GTPases. Together with GTPase activating proteins (GAPs) they control the activity of monomeric GTPases and thus, cellular responses such as migration and proliferation. It becomes more and more evident that not the global activity of the GTPases, but the local activation in subcellular compartments is critical for the adequate cellular responses and pathological alterations.
We are therefore interested in the local regulation of the activity of the GTPase RhoA at endothelial adherens junctions by the poorly characterized GEF RhoGEf17 and p190RhoGAP. With regard to endothelial activation we are further interested in the role of the cAMP-dependent Rap-GEF EPAC1.
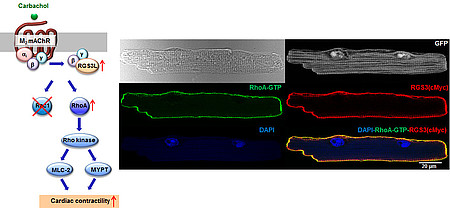
RGS3L in cardiac contractility
RGS3L is an unusual RGS protein which by binding of Gβγ dimers can switch the activation of monomeric GTPases of the Rho family by classical cardiac Gi-coupled receptors like muscarinic M2 receptors (M2R), from Rac1 to RhoA. RGS3L is up-regulated in human heart failure und by cardiac resynchronization therapy. As in a heart failure model and in the neonatal heart a RhoA-Rho kinase (ROCK) dependent positive inotropic effect of M2R stimulation occurs the up-regulation of RGS3L might cause beneficial counter-regulatory effect in heat failure. In this project, we investigate the underlying mechanism and a potential therapeutic value of this pathway.
Recent Publications
- Arnold, C., Demirel, E., Feldner, A., Genové, G., Zhang, H., Sticht, C., Wieland, T., Hecker, M., Heximer, S. & Korff, T. (2018) Hypertension-evoked RhoA activity in vascular smooth muscle cells requires RGS5. FASEB J., 32, 2021-2035
- Zhao, Z., Lan, H., El-Battrawy, I., Li, X., Buljubasic, F., Sattler, K. Yücel, G., Lang, S., Tiburcy, M., Zimmermann, W. H., Cyganek, L., Utikal , J., Wieland, T., Borggrefe, M., Zhou X.-B. & Akin, I. (2018) Ion channel expression and characterization in human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes. Stem Cell Int, 2018, 6067096
- Schrade, K,. Tröger, J., Eldahshan, A., Zühlke, K., Abdul Azeez, K. R., Elkins, J. M., Neuenschwander, M., Oder, A., Elkewedi, M., Jaksch, S., Andrae, K., Li, J., Fernandes, J., Müller, P. M., Grunwald, S., Marino, S. F., Vukićević, T., Eichhorst, J., Wiesner, B., Weber, M., Kapiloff, M., Rocks, O., Daumke, O., Wieland, T., Knapp, S., von Kries, J. P. & Klussmann, E. (2018) An AKAP-Lbc-RhoA interaction inhibitor promotes the translocation of aquaporin-2 to the plasma membrane of renal collecting duct principal cells. PLoS One., 13, e0191423
- El-Battrawy, I., Zhao, Z., Lan, H., Li, X., Yücel, G., Lang, S., Sattler, K., Schünemann, J. D., Zimmermann, W. H., Cyganek, L., Utikal, J., Wieland, T., Bieback, K., Bauer, R., Ratte, A., Pribe-Wolferts, R., Rapti, K., Nowak, D., Wittig, J., Thomas, D., Most, P., Katus, H. A., Ravens, U., Schmidt, C., Borggrefe, M., Zhou, X. B., Müller, O. J. & Akin, I. (2018) Ion Channel Dysfunctions in Dilated Cardiomyopathy in Limb-Girdle Muscular Dystrophy. Circ Genom Precis Med., 11, e001893
- El-Battrawy, I., Zhao, Z., Lan, H., Cyganek, L., Tombers, C., Li, X., Buljubasic, F., Lang, S., Tiburcy, M., Zimmermann, W. H., Utikal, J., Wieland, T., Borggrefe, M., Zhou, X. B. & Akin, I. (2018) Electrical dysfunctions in human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes from a patient with an arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy. Europace., doi: 10.1093/europace/euy042.
- El-Battrawy, I., Lan, H., Cyganek, L., Zhao, Z., Li, X., Buljubasic, F., Lang, S., Yücel, G., Sattler, K., Zimmermann, W. H., Utikal, J., Wieland, T., Ravens, U., Borggrefe, M., Zhou, X. B. & Akin, I. (2018) Modeling Short QT Syndrome Using Human-Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes. J Am Heart Assoc., 7, pii: e007394
- Toth D. A., Schell R., Levay M., Vettel C., Theis P., Haslinger, C., Alban, F., Werhahn, S., Frischbier, L., Krebs-Haupenthal, J., Thomas, D., Gröne, H. J., Avkiran, M., Katus H. A., Wieland, T. & Backs, J. (2018) Inflammation leads through PGE/EP3 signaling to HDAC5/MEF2-dependent transcription in cardiac myocytes. EMBO Mol. Med., DOI:10.15252/emmm.20170853
- Abu-Taha IH, Heijman J, Hippe HJ, Wolf NM, El-Armouche A, Nikolaev VO, Schäfer M, Würtz C, Neef S, Voigt N, Baczkó I, Varró A, Müller M, Meder B, Katus HA, Spiger K, Vettel C, Lehmann LH, Backs J, Skolnik EY, Lutz S, Dobrev D, Wieland T. Nucleoside Diphosphate Kinase-C Suppresses cAMP Formation in Human Heart Failure. Circulation. 2017 Feb 28;135(9):881-897
- Beck SC, Feng Y, Sothilingam V, Garcia Garrido M, Tanimoto N, Acar N, Shan S, Seebauer B, Berger W, Hammes HP, Seeliger MW. Long-term consequences of developmental vascular defects on retinal vessel homeostasis and function in a mouse model of Norrie disease. PLoS One. 2017 Jun 2;12(6):e0178753.
- Dewenter M, Neef S, Vettel C, Lämmle S, Beushausen C, Zelarayan LC, Katz S, von der Lieth A, Meyer-Roxlau S, Weber S, Wieland T, Sossalla S, Backs J, Brown JH, Maier LS, El-Armouche A. Calcium/Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinase II Activity Persists During Chronic β-Adrenoceptor Blockade in Experimental and Human Heart Failure. Circ Heart Fail. 2017 May;10(5):e003840
Kontextspalte
Group Leader

Thomas Wieland, PhD